Paper archives and libraries hold millions of books, dissertations, monographs, and paper documents that form humanity’s knowledge base. Still, much of this material remains in paper form. Therefore, finding, retrieving, and analyzing required information can take weeks or even months. It is a problem for users who have deadlines and timeframes for obtaining valuable insights.
Let’s delve into why digitizing documents and archives is a challenge, not only due to the volume of materials. But at the end of the day, it brings a particular value to all parties concerned. We’ll explain below how to avoid traditional manual scanning, which is time-consuming and prone to errors. And how digital transformation and AI-powered tools make document digitalization a proper alternative.
Why Digitizing Is Not the Same as Scanning
Some of us mistakenly believe that document digitization means scanning papers into PDFs. But document digitization transforms information into machine-readable, AI-ready data that can be searched, analyzed, and integrated into automated workflows.
| Scanned files | Digitization process | |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Creates a visual copy of a document | Converts documents into structured, searchable, AI-ready data |
| Output | PDF or JPEG | Searchable PDFs, JSON, XML, TXT, embeddings, metadata |
| Searchability | Not searchable without OCR | Fully searchable via OCR and semantic indexing |
| Data Usability | Limited; looks like a scanned image | Enables AI-powered search, classification, and analytics |
| Integration | No integration with enterprise systems | Connects seamlessly to data lakes, LLMs, and RAG platforms |
| Compliance & Preservation | Basic storage capabilities | Ensures ISO-compliant formats, metadata, and secure archives |
Challenges in Digitizing Archives
Digitizing paper files and archives presents numerous challenges, including handling fragile documents, managing large volumes of data, and maintaining consistency throughout the process. What are the challenges, and how do you find the right software or provider for document scanning services?
Fragile and Damaged Documents |
Experts must handle fragile and damaged documents with care during scanning. Archives follow best practices for handling these items, such as wearing gloves, supporting documents with rigid backing, and using special containers for transport. Professional teams that digitize paper documents combine careful handling with scanning strategies to get the job done. |
Large Volumes of Data |
An automated document management system can help with large amounts of data by providing storage space, minimising human intervention and errors, and reprocessing digital files. |
Ensuring Consistent Quality |
Ensuring consistency in digitizing documents involves:
|
To achieve high accuracy, speed, and preservation standards, as executers we rely on combination of robotic scanners, industrial feed devices, OCR servers, and AI-driven automation tools. The choice of equipment defines the efficiency of the entire workflow—from how gently a fragile book is scanned to how quickly its content becomes searchable and ready for AI processing.
Equipment and Infrastructure for High-Volume Digitization
| Category | Model / Tool | Speed and Features | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Robotic Book Scanners | ScanRobot SR301 | 3,000 pages/hour, automatic page turning, V-cradle 60°–90°, non-destructive | Fragile books, bound archives |
| Kirtas APT 2400 | Dual-camera capture, 2,400 pages/hour | Standard archival documents | |
| Treventus ScanRobot | V-shape for rare collections | Historical and museum archives | |
| DL Mini (Qidenus) | Compact semi-automatic, 1,500 pages/hour | Small archives, research labs |
ScanRobot SR301
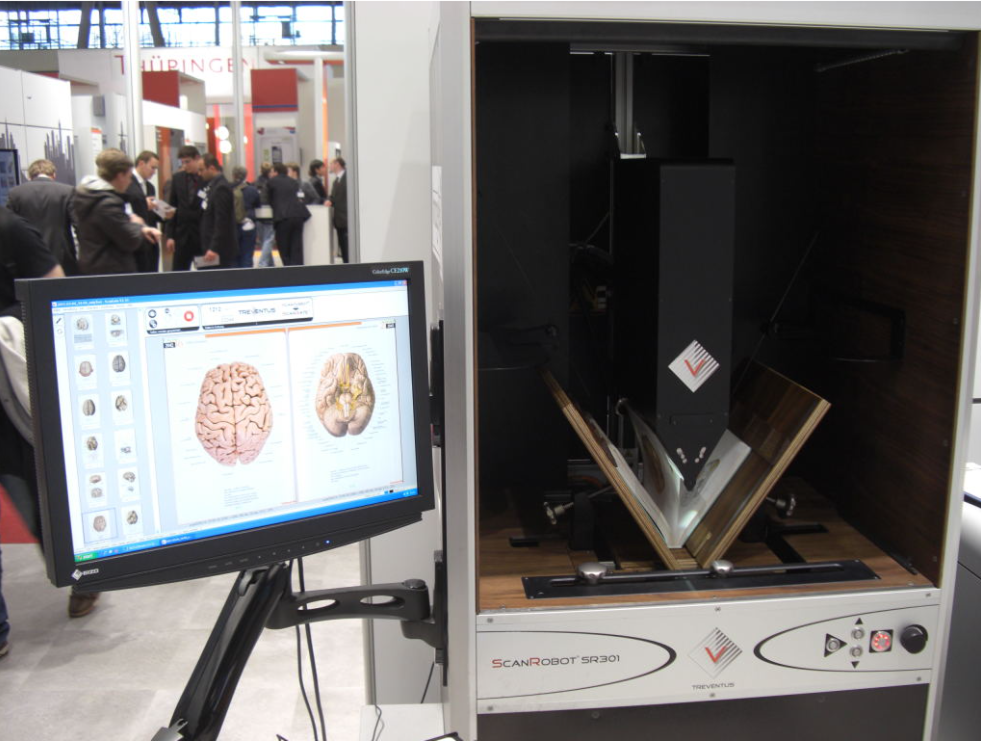
Source: grufo
Kirtas APT 2400
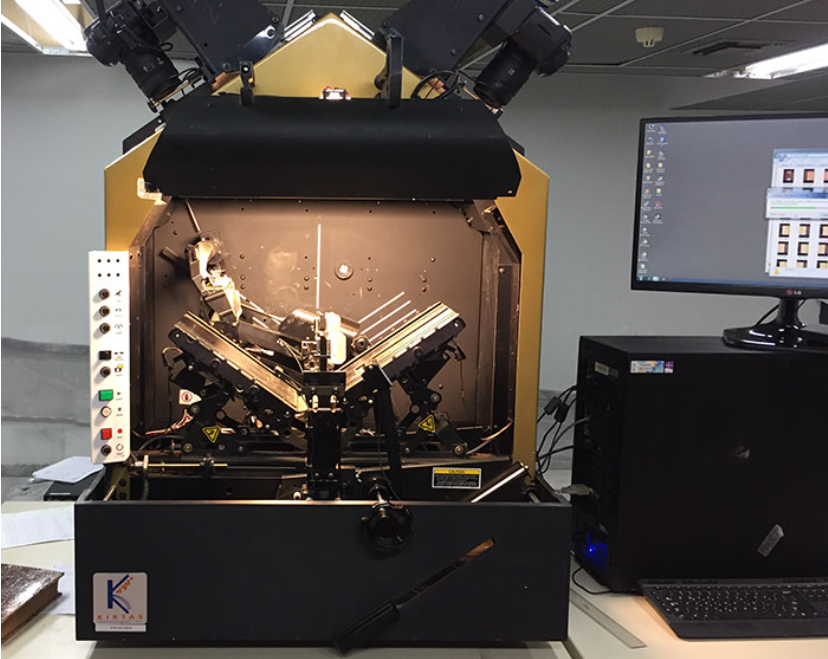
Source: typorama
Treventus ScanRobot

Source: treventus
DL Mini

Source: walternagel
| Category | Model / Tool | Speed and Features | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-Speed Feed Scanners | Fujitsu fi-7900 / fi-8950 | 140–160 pages/min | Office archives, A4/A3 formats |
| Kodak i4250 / i5850 | Up to 210 pages/min | Large-scale digitization | |
| Canon DR-G2140 | Up to 280 pages/min | Universal document scanning |
Fujitsu fi-8950

Source: pfu
| OCR & Post-Processing Software | ABBYY FineReader Server | Enterprise OCR, 95%+ accuracy, automation scripting | Centralized OCR processing |
| Tesseract (Open Source) | Flexible pipeline for AI/NLP integration | AI-ready OCR tasks | |
| IRIS / Rakuten / Azure Form Recognizer | Cloud OCR, multilingual | Scalable document recognition |
Who Needs to Digitize Documents
In theory, every authority, company, or user prefers digital documents to handle large volumes of documents and information, but for some sectors or fields, it has become critical:
Government and Public Institutions
National archives, municipal registries, and cultural heritage institutions rely on digitization to preserve critical records, comply with transparency regulations, and provide public access to historical, geospatial, and business-related data.
Healthcare
Hospitals, clinics, and research labs need to digitize patient records, lab results, and clinical reports, enable AI-driven diagnostics, and provide a knowledge base for medical staff and patients to access helpful information through developed responders and chatbots.
Energy, Mining Businesses, and Manufacturing
In industries that manage technical archives, such as geological reports, maps, and geospatial data, digitization enhances decision-making, predictive maintenance, and AI-driven exploration, as shown below in LaSoft’s GeoAI project.
Education and Research Centres
Universities, libraries, and research centres benefit from making theses, scientific papers, and rare manuscripts machine-readable for indexing, semantic search, and AI-based knowledge extraction.
Financial and Insurance
Banks, insurers, and investment companies manage millions of contracts, claims, and compliance reports. Secure digital delivery speeds up onboarding, fraud detection, claims automation, and risk analysis.
Legal Institutions
Courts and law firms that handle paper records, sensitive data, agreements, patents, and litigation documents. Digital versions in AI-ready formats accelerate case preparation and search, and facilitate secure document sharing.
How AI Improves the Scanning Workflow
Artificial intelligence transforms digitization by enabling a fully automated content-scanning pipeline. It combines computer vision, machine learning, and natural language processing to help extract the required information.
1. Document Structure Recognition
AI algorithms detect and interpret a document’s internal structure: titles, subtitles, paragraphs, tables, etc. It helps to reconstruct logical hierarchies. The vendor can use tools such as ABBYY FineReader Server, Azure Form Recognizer, or custom transformer models trained on datasets to identify patterns and layouts typical of technical reports, scientific articles, or handwritten archives.
2. Image Enhancement
Computer vision helps automatically fix visual imperfections such as page shadowing, glare, uneven lighting, and noise. For fragile or curved pages, V-shaped book scanners combined with AI correction ensure non-destructive handling while maintaining readability.
3. AI-Powered OCR and Handwriting Recognition
Deep learning models bring OCR to the next level. Modern AI-based OCR engines not only recognize printed fonts but also interpret historical handwriting, faded ink, and multilingual text.
4. Intelligent Document Classification
AI models classify documents by type and purpose, after experts extract the text. It defines if it’s reports, contracts, monographs, drawings, maps, etc. Using machine learning classifiers, each document receives tags and metadata describing its content, domain, and intended use.
5. Semantic Tagging
Natural Language Processing (NLP) models extract entities, relationships, and contextual metadata. For example, in geological archives, the system identifies names of mineral deposits, coordinates, and chemical compounds.
6. Automated Quality Control
AI assists human operators in evaluating image quality, OCR confidence levels, and metadata consistency. It flags low-quality pages for reprocessing.
Paper Documents Digitization as part of Digital Transformation
Making digitized archives online involves creating user-friendly interfaces, implementing searchable databases, and securing online access. These steps ensure that digitized archives reach a wider audience and remain accessible over time, unlike scanned documents. Creating a usable software product for the end user to get answers to their questions in the form of text documents and digital images depends on the software development team you choose.
User-Friendly Interfaces |
A website interface that incorporates digital records and images reduces paper waste, supports sustainability, and ensures that sensitive information remains secure. It should have intuitive navigation and chatbot features, allowing all users to benefit from workflow automation, receive accurate answers based on integrated knowledge bases, and access relevant content resources. |
Integrating Searchable Databases |
Searchable databases allow users to find specific digital format records quickly. Digitization is a more convenient solution than document scanning services as it provides rapid access to records through indexed searches, reducing manual retrieval time significantly. |
Securely Stored with Online Access |
Securing online access involves:
|
The Process of Document Digitization Based on Lasoft Experience
Digitizing archives is a multi-stage process that converts physical copies into searchable, AI-ready digital assets. Benefits are apparent, as this process helps avoid document loss and security risks and increases efficiency by providing on-demand access to information. At LaSoft, we follow a seven-step methodology to ensure data accuracy, accessibility, and security. Our process of digitalizing documents transforms historical archives into AI-ready ecosystems.
1. Document Preparation |
Before any scanning begins, documents are carefully prepared to ensure optimal quality and prevent damage:
This meticulous preparation ensures every file is cataloged, trackable, and ready for automation. |
2. Robotic Scanning |
Unlike traditional scanning, we use robotic V-shaped scanners designed for high-speed, non-destructive digitization:
This approach guarantees efficiency and preservation, making it ideal for archives containing fragile historical materials. |
3. OCR and Intelligent Analysis |
Once documents are scanned, they must become machine-readable. We implement advanced OCR (Optical Character Recognition) and analysis pipelines:
This step transforms static images into structured, usable information. |
4. Quality Control |
Accuracy is essential. Our AI-assisted algorithms automatically identify and fix:
Human specialists review flagged cases to ensure error-free datasets ready for semantic search. |
5. Semantic Tagging and Metadata Enrichment |
Digitization doesn’t end with readable text. LaSoft enhances archives with semantic context to make data truly intelligent:
This process allows searching by meaning, not just keywords, and supports LLM-powered assistants. |
6. Archiving and Secure Storage |
Digitized documents are stored in standardized, compliant formats:
This guarantees data security, compliance, and future-proof access. |
7. Vectorization and AI Integration |
The final stage converts archives into AI-ready knowledge systems:
|

Real-Life Case Study: LaSoft’s GeoAI Platform for Geological Document Digitization
National geological archives often hold decades of irreplaceable scientific data, stored in diverse formats such as paper reports, technical documentation, scanned maps, and handwritten field notes. In many countries, these archives are stored in analog formats, making it nearly impossible to access insights at scale.
Setting the Goal
Traditionally, retrieving information from geological archives required manually searching through thousands of PDFs, images, or even physical records to locate specific data points. This slow, fragmented process led to missed insights, duplicated efforts, and delayed decision-making.
To solve this challenge, LaSoft partnered with a client to create an AI-driven geospatial platform designed to digitize, index, and intelligently interpret geological documents. By combining natural language processing (NLP), semantic search, and interactive geodata viewers, the solution transforms unstructured archives into a dynamic, intelligent knowledge ecosystem.
How the Solution Works
LaSoft’s solution is powered by a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) architecture, tailored specifically for the geosciences. Unlike generic AI tools, this platform is fully integrated with domain-specific workflows, terminology, and data formats used by geological organizations.
Here’s how the system operates:
| Digitization and Semantic Indexing | All geological documents are digitized, processed via OCR, and broken into smaller, meaningful “chunks” of information. |
| Expert Validation | Each chunk is reviewed and verified by professional geologists before being indexed, ensuring the accuracy and trustworthiness of the data. |
| AI-Powered Retrieval | When a user asks a question in natural language, the platform detects relevant chunks and inputs them into a Large Language Model (LLM). |
| Accurate Responses | The LLM constructs a context-aware answer supported by source citations for full traceability. The meaningful outcome users get: instead of spending days locating relevant insights, researchers now get accurate, verified answers in seconds. |
Transforming Geological Archives into Intelligent Assets
LaSoft’s GeoAI platform has transformed static archives into an AI-powered assistant that serves researchers, government institutions, and private enterprises.
LaSoft has delivered a solution that integrates digitization technologies, semantic AI models, and human expertise. The result is a future-proof geoscientific knowledge system that enables more intelligent decisions, faster discoveries, and stronger collaboration across sectors.



